- | 8:30 am
All those microplastics in the ocean could be spreading disease-causing parasites
Pathogens from land can hitch a ride to the beach on microplastics, providing a new way for germs to concentrate along coastlines and travel to the deep sea.

Typically, when people hear about plastic pollution, they might envision seabirds with bellies full of trash or sea turtles with plastic straws in their noses. However, plastic pollution poses another threat that’s invisible to the eye and has important consequences for both human and animal health.
Microplastics, tiny plastic particles present in many cosmetics, can form when larger materials, such as clothing or fishing nets, break down in water. Microplastics are now widespread in the ocean and have been found in fish and shellfish, including those that people eat.
As researchers studying how waterborne pathogens spread, we wanted to better understand what happens when microplastics and disease-causing pathogens end up in the same body of water. In our recent study published in the journal Scientific Reports, we found that pathogens from land can hitch a ride to the beach on microscopic pieces of plastic, providing a new way for germs to concentrate along coastlines and travel to the deep sea.
[Photo: The Conversation]
INVESTIGATING HOW PLASTICS AND PATHOGENS INTERACT
We focused on three parasites that are common contaminants in marine water and seafoods: the single-celled protozoans Toxoplasma gondii (Toxo), Cryptosporidium (Crypto) and Giardia. These parasites end up in waterways when feces from infected animals, and sometimes people, contaminate the environment.
Crypto and Giardia cause gastrointestinal disease that can be deadly in young children and immunocompromised individuals. Toxo can cause lifelong infections in people, and can prove fatal for those with weak immune systems. Infection in pregnant women can also cause miscarriage or blindness and neurological disease in the baby. Toxo also infects a wide range of marine wildlife and kills endangered species, including southern sea otters, Hector’s dolphins, and Hawaiian monk seals.
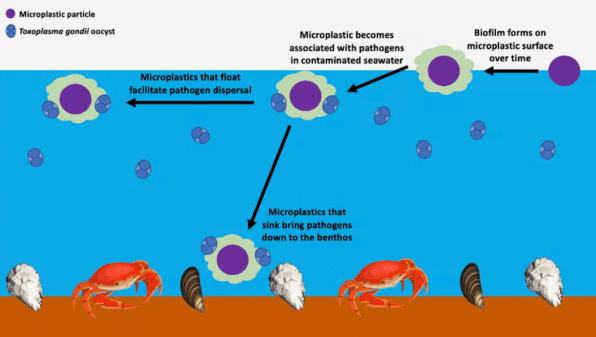
To test whether these parasites can stick onto plastic surfaces, we first placed microplastic beads and fibers in beakers of seawater in our lab for two weeks. This step was important to induce the formation of a biofilm—a sticky layer of bacteria and gel-like substances that coats plastics when they enter fresh or marine waters. Researchers also call this sticky layer an eco-corona. We then added the parasites to the test bottles and counted how many became stuck on the microplastics or remained freely floating in the seawater over a seven-day period.
We found that significant numbers of parasites were clinging to the microplastic, and these numbers were increasing over time. So many parasites were binding to the sticky biofilms that, gram for gram, plastic had two to three times more parasites than did seawater.
Surprisingly, we found that microfibers (commonly from clothes and fishing nets) harbored a greater number of parasites than did microbeads (commonly found in cosmetics). This result is important because microfibers are the most common type of microplastic found in marine waters, on coastal beaches, and even in seafood.
PLASTICS COULD CHANGE OCEAN DISEASE TRANSMISSION
Unlike other pathogens that are commonly found in seawater, the pathogens we focused on are derived from terrestrial animal and human hosts. Their presence in marine environments is entirely due to fecal waste contamination that ends up in the sea. Our study shows that microplastics could also serve as transport systems for these parasites.
These pathogens cannot replicate in the sea. Hitching a ride on plastics into marine environments, however, could fundamentally alter how these pathogens move around in marine waters. We believe that microplastics that float along the surface could potentially travel long distances, spreading pathogens far from their original sources on land and bringing them to regions they would otherwise not be able to reach.
On the other hand, plastics that sink will concentrate pathogens on the sea bottom, where filter-feeding animals like clams, mussels, oysters, abalone, and other shellfish live. A sticky biofilm layer can camouflage synthetic plastics in seawater, and animals that typically eat dead organic material may unintentionally ingest them. Future experiments will test whether live oysters placed in tanks with and without plastics end up ingesting more pathogens.
A ONE HEALTH PROBLEM
One Health is an approach to research, policy, and veterinary and human medicine that emphasizes the close connection of animal, human, and environmental health. While it may seem that plastic pollution affects only animals in the ocean, it can ultimately have consequences on human health.
Our project was conducted by a multidisciplinary team of experts, ranging from microplastics researchers and parasitologists to shellfish biologists and epidemiologists. This study highlights the importance of collaboration across human, animal, and environmental disciplines to address a challenging problem affecting our shared marine environment.
Our hope is that better understanding of how microplastics can move disease-causing pathogens in new ways will encourage others to think twice before reaching for that plastic straw or polyester T-shirt.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.